| CHAPTER
6 XMP Controller Motion Drive I/O |
|
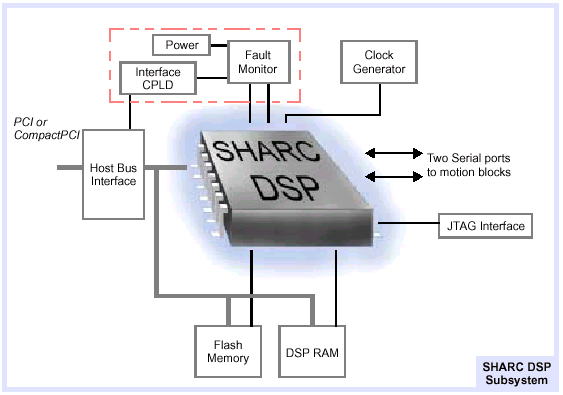
SHARC DSP Processor SubsystemThe DSP processor subsystem includes the following subsystems:
SHARC DSP ProcessorThe XMP's main DSP processor is a 32-bit Analog Devices 21061 Floating Point DSP (also known as the SHARC DSP) with a peak performance of 150 MFLOPs. The 21061 provides trajectory planning, coordination, interpolation and position/ velocity loop closure. DSP RAMExternal SRAM is available to the DSP for maintaining message buffers and storing data. The SRAM can be up to 2 Mbytes of zero-wait state RAM. The standard configuration is 64K x 32 bit words (256K bytes). Flash MemoryAn 8-Mbit FLASH memory stores the DSP boot code, FPGA configuration code and nonvolatile system information. The FLASH memory is rated for 100,000 write/erase cycles. Serial Ports to Motion BlocksThe SHARC DSP communicates with the four peripheral motion blocks over two 40 Mbit/sec serial links. All DSP-to-motion block data transfers occur over these two links.
Each SHARC DSP serial port connects to two motion blocks. The motion blocks are the gateways for all of the controller's I/O to the external system. |
|