| CHAPTER 2 Motion Console |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| If the axis is close to completing a move when E-Stop is activated, the axis may halt before the E-Stop Time has expired. |
Normal Feedrate-- Speed
scaling factor applied to movement. 0 = stopped; 1 = normal
speed (unscaled); 1.5 = 150%; 2 = 200%, -1 = reversed norma
speed; etc.
Delay-- Time delay (in
seconds) before execution of next move command. If operating
in Repeat Mode, the delay will be applied to the beginning
of each move segment.
Panic Action-- Action to
execute when the <F12> panic key is activated.
| Some panic action states (E-Stop and Abort) flag a fault condition. To reset the system after a fault, click on the Clear Fault button (MS Summary / Actions tab page). |
- None-- Motion is halted at the end of the currently commanded move. (No-fault condition.)
- Stop-- Motion is halted using a Stop. (No-fault condition.)
- E-Stop-- Motion is halted using an E-Stop, and a fault condition is flagged.
- E-Stop, Abort-- Motion is halted using both an E-Stop and an Abort, and a fault condition is flagged. A fault condition is flagged.
- Abort-- Motion is halted using an Abort.
Configuration Attributes: "Actions" Tab Page
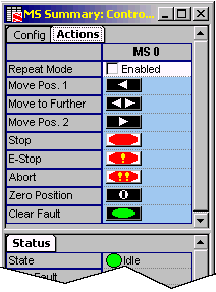
Repeat
Mode-- [Enabled; (not enabled)] Repeats programmed
motion.
| Each repeated motion will be delayed by the Delay amount (see description above on Delay). |
 Move Pos. 1-- Command
each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor to Position
1.
Move Pos. 1-- Command
each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor to Position
1.
 Move to Further--
Command each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor to
either Position 1 or Position 2, whichever is
further away.
Move to Further--
Command each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor to
either Position 1 or Position 2, whichever is
further away.
 Move Pos. 2-- Command
each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor to Position
2.
Move Pos. 2-- Command
each axis associated with the Motion Supervisor to Position
2.
 Stop -- Stops movement
of objects under control of current Motion Supervisor within
Stop time (seconds).
Stop -- Stops movement
of objects under control of current Motion Supervisor within
Stop time (seconds).
 E-Stop -- Emergency
stop. Halts movement of objects under control of current Motion
Supervisor within E-Stop time (seconds) and leaves the axes
in an Error state.
E-Stop -- Emergency
stop. Halts movement of objects under control of current Motion
Supervisor within E-Stop time (seconds) and leaves the axes
in an Error state.
| E-Stop does NOT disable closed-loop control and does not disable the amp enable output(s). |
 Abort -- Immediately
stops movement of objects under control of current Motion
Supervisor, disables closed-loop control, and disables the
amp enable output(s), leaving the axes in an Error
state.
Abort -- Immediately
stops movement of objects under control of current Motion
Supervisor, disables closed-loop control, and disables the
amp enable output(s), leaving the axes in an Error
state.
 CAUTION!
Do not use Abort when testing equipment which depends
upon servos or stepper motors to secure personnel or equipment
(e.g., lifting cranes, elevators, etc.). The Abort
command disables servos and steppers and, in some circumstances,
may present a hazard to personnel or equipment due to sudden
loss of power.
CAUTION!
Do not use Abort when testing equipment which depends
upon servos or stepper motors to secure personnel or equipment
(e.g., lifting cranes, elevators, etc.). The Abort
command disables servos and steppers and, in some circumstances,
may present a hazard to personnel or equipment due to sudden
loss of power.
 Zero Position--
Sets the origin of the axis to the current actual position
and the command position to 0. The algorithm for setting the
origin is:
Zero Position--
Sets the origin of the axis to the current actual position
and the command position to 0. The algorithm for setting the
origin is:
new origin = current origin + actual position
Status Attributes
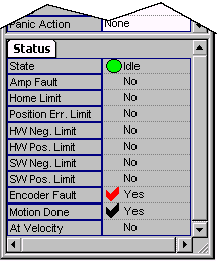
State -- Current motion state. (See Motion States table below.)
|
Stopping. (State parameter). Motion has been commanded to stop. |
|
|
Moving when not commanded to move. NOTE: This occurs when another application commands a move. |
|
 Motion Supervisor Object
Motion Supervisor Object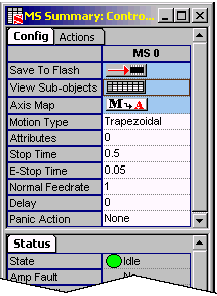
 Save to Flash-- Pre-selects current Motion Supervisor
settings for saving to flash memory. For more information
on using Save to Flash, see description in the first part
of this chapter.
Save to Flash-- Pre-selects current Motion Supervisor
settings for saving to flash memory. For more information
on using Save to Flash, see description in the first part
of this chapter. View Sub-objects-- Shows all sub-objects for the Motion
Supervisor. For more information, see
View Sub-objects-- Shows all sub-objects for the Motion
Supervisor. For more information, see  Axis Map-- Displays the MS Axis List Configuration window.
For more information, see
Axis Map-- Displays the MS Axis List Configuration window.
For more information, see 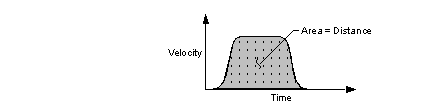
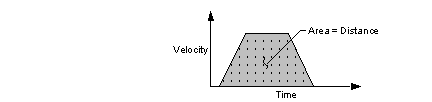
 CAUTION!
Actual stopping time is limited by mass and speed! If you
are moving a heavy object at high speed and command a very
rapid Stop Time, your motion control or mechanical
system may be unable to comply. Verify that drive and motor
manufacturer's specifications meet the demands placed upon
your system BEFORE assuming a stop time.
CAUTION!
Actual stopping time is limited by mass and speed! If you
are moving a heavy object at high speed and command a very
rapid Stop Time, your motion control or mechanical
system may be unable to comply. Verify that drive and motor
manufacturer's specifications meet the demands placed upon
your system BEFORE assuming a stop time. Clear Fault--
Clears the Motion Supervisor's error state and all sub-object
Clear Fault--
Clears the Motion Supervisor's error state and all sub-object